Monderma
Monderma- 21 Apr 2025
- UVA reaches deep into skin
- UVB burns the surface layer
- UVC is filtered yet hazardous
- Each light type affects cells
- Knowledge supports care with Monderma
Ultraviolet light appears in daily life through sunlight and artificial sources, so understanding its behaviour helps readers protect their skin with confidence. These light types influence ageing, comfort, and long term skin health.
In this article, we explain the key properties of UVA, UVB, and UVC. You will see how each wavelength affects the skin, how to approach protection, and why informed choices improve resilience over time.
Understanding UV Light
UV light sits beyond the visible spectrum and includes UVA, UVB, and UVC. Each type interacts with skin differently. UVA reaches deeper layers, while UVB affects the surface. UVC rarely reaches the ground due to ozone filtering.
These wavelengths influence collagen, comfort, and cell stability. They also appear in medical and industrial settings, which highlights their wide impact on health and daily routines [1].
UVA Light & Skin Ageing
UVA accounts for most UV radiation reaching the ground and can pass through glass and clouds. This means daily exposure occurs even indoors or in cooler weather [1,4].
UVA moves into the dermis where collagen and elastin sit. Over time this contributes to visible signs of ageing. UVA also links with DNA damage and skin cancers when exposure accumulates [1].
UVA Features
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Penetration | Reaches the dermis and passes through glass and clouds [1,4] |
| Health impact | Contributes to ageing and plays a role in skin cancer [1] |
Table 1: UVA characteristics
UVA Uses
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Medical use | Appears in PUVA therapy for psoriasis and vitiligo under guidance [3] |
Table 2: UVA uses
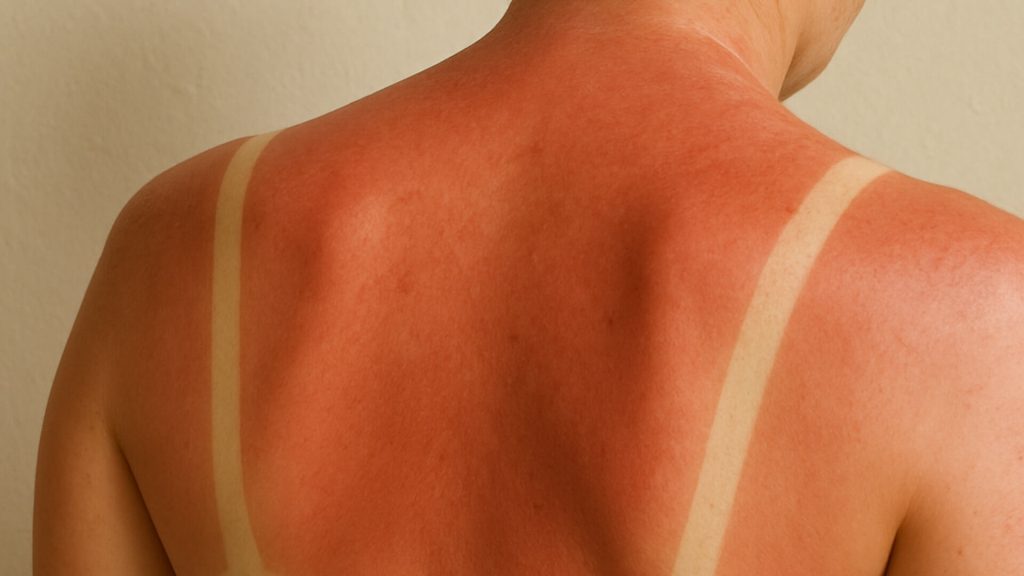
UVB Light & Surface Damage
UVB focuses on the outer skin layers and increases during midday sun. This wavelength is responsible for sunburn and plays a central role in DNA mutation leading to skin cancer [1,4].
UVB also supports vitamin D synthesis with brief, safe exposure. Medical teams use narrow band UVB therapy to treat psoriasis and eczema, improving symptoms in controlled settings [5].
UVB Features
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Penetration | Affects the epidermis and varies with time and season |
| Health impact | Causes burns and contributes to skin cancer risk [3] |
Table 3: UVB characteristics

UVB Uses
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Medical use | NB UVB therapy treats psoriasis and eczema with monitored care [5] |
Table 4: UVB uses
UVC Light & Hazard Risk
UVC does not naturally reach the skin because the ozone layer absorbs it. Artificial UVC appears in specialised lamps used for disinfection due to its strong ability to disrupt cellular DNA [1,7].
Although useful in enclosed systems, UVC exposure remains unsafe for the skin and eyes. Even short contact may cause burns or photokeratitis, so strict handling measures are essential [3,7].
UVC Features
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Penetration | Blocked by the atmosphere and seen only in artificial devices |
| Health impact | Causes burns and eye injury with no safe direct exposure [7] |
Table 5: UVC characteristics

UVC Uses
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Industrial use | Disinfects air, water, and surfaces in controlled systems |
Table 6: UVC uses
Comparing UVA, UVB & UVC
UVA moves deepest and contributes strongly to ageing. UVB affects the surface and causes burns. UVC is blocked naturally yet highly harmful when used in artificial devices.
Understanding these differences helps readers tailor protection to daily needs and recognise when specialist care or precautions are required.
UV Comparison Table
| Type | Summary |
|---|---|
| UVA | Reaches dermis and contributes to ageing [1] |
| UVB | Causes burns and supports vitamin D formation [4] |
Table 7: UVA and UVB comparison
| Type | Summary |
|---|---|
| UVC | Hazardous artificial light used for disinfection [7] |
| Protection | Sunscreen, clothing, shade, and avoidance for UVC |
Table 8: UVC comparison
Protection & Skin Health
Consistent sun protection helps reduce the impact of UVA and UVB on collagen, pigmentation, and long term skin stability. Sunscreen, clothing, and shade improve comfort and resilience through daily habits [8].
Moisturising and gentle routines help maintain the skin barrier after exposure. These steps support calm, stable skin and reduce irritation linked with environmental stress.
Conclusion
UV light influences skin health in different ways. UVA contributes to deeper ageing, UVB supports vitamin D formation at the surface, and UVC is used for disinfection but should never contact skin or eyes. Understanding these differences helps maintain safe, balanced exposure.
If you would like personalised skincare that reflects your own needs, you can explore a custom formula through Monderma.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Solar and ultraviolet radiation.
- Grossman DC, et al. Behavioral counseling to prevent skin cancer. JAMA.
- World Health Organization. Ultraviolet radiation.
- Goulden V, et al. British Photodermatology Group guidelines for NB UVB.
- Newcastle Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Narrowband ultraviolet B treatment.
- Dai T, et al. Ultraviolet C irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol B.
- NHS. Sunscreen and sun safety.
Join the Newsletter
Insights that make your skin feel understood