Monderma
Monderma- 11 Apr 2025
- Trifarotene is a targeted retinoid
- It acts selectively on RAR-γ receptors
- Trifarotene improves acne with fewer side effects
- It is more tolerable compared to tretinoin
- Monderma compounds selected retinoids
In dermatology, new treatments often offer significant advancements in managing skin conditions. Trifarotene is a fourth-generation retinoid that is gaining attention for its selective mechanism in treating acne and other skin concerns.
In this article, we explore how trifarotene works, compare it with other retinoids like tretinoin, and discuss the benefits it offers for those with acne and sensitive skin.
Mechanism Of Action
Trifarotene is a fourth-generation retinoid that selectively activates the retinoic acid receptor gamma (RAR-γ) [1,2]. This specificity distinguishes it from earlier retinoids, which affect multiple receptor subtypes, increasing the potential for side effects [1,2].
By binding specifically to RAR-γ, trifarotene promotes skin cell turnover and reduces inflammation, helping treat acne without the widespread effects typical of other retinoids [2,4]. Its targeted action minimizes systemic absorption, lowering the risk of side effects [3,4].
Trifarotene Vs Tretinoin
Tretinoin is a widely used retinoid for acne but has a broader mechanism of action, affecting multiple retinoic acid receptors (RAR-α, RAR-β, RAR-γ) [1,3]. While effective, this non-selective activity can cause skin irritation and peeling, making it less suitable for sensitive skin [1,2,3].
Trifarotene’s selective targeting of RAR-γ offers a more refined therapeutic profile. It is effective in reducing both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions while being better tolerated by those with sensitive skin [3,4]. However, direct comparative trials with tretinoin are still lacking [3,4].
Trifarotene Vs Tretinoin Comparison
| Feature | Trifarotene | Tretinoin |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | Fourth-generation retinoid [1,2,3] | First-generation retinoid [1,2] |
| Receptor Selectivity | Highly selective for RAR-γ [1,2,3] | Non-selective, binds all RAR subtypes [1,2,3] |
| Approved Indications | Acne (facial, truncal) [2,3] | Acne, other skin conditions [1,2] |
| Efficacy | Reduces inflammatory/non-inflammatory lesions [3,4] | Effective in acne, broad benefits [1,2] |
| Side Effect Profile | Lower irritation, erythema, peeling [3,4] | More irritation, redness, peeling [1,2,3] |
| Systemic Absorption | Low, minimal plasma levels [3,4] | Moderate, higher risk with body use [1,4] |
| Use in Sensitive Skin | Preferable for sensitive skin [3,4] | May cause irritation in sensitive skin [1,3] |
Table 1: Trifarotene vs Tretinoin
Efficacy & Safety
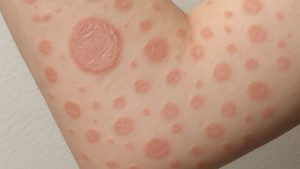
Trifarotene has demonstrated significant efficacy in clinical trials for acne, with a lower incidence of adverse effects compared to tretinoin [3,4]. In phase III trials, trifarotene cream applied once daily showed success rates of 29.4% for facial acne and 42.3% for truncal acne, outperforming vehicle creams [3].
Its efficacy extends beyond acne treatment, as it may help reduce atrophic acne scars. A phase IV study demonstrated a 24% reduction in scar count after 24 weeks of trifarotene treatment [5]. Common side effects include mild erythema, scaling, and dryness [3,4].
Benefits Of Trifarotene
Targeted Skin Treatment
Trifarotene provides a targeted treatment for acne by focusing on RAR-γ receptors. This selective action confines its therapeutic effects to the skin, minimizing the risk of systemic side effects and improving adherence [2,4].
Comprehensive Acne Management
Trifarotene is effective for both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions, offering a comprehensive treatment approach. It reduces inflammation, promotes skin cell turnover, and addresses the root causes of acne [3,5].
Improved Tolerability
One of the key benefits of trifarotene is its improved tolerability. Unlike other retinoids, it causes fewer irritations, making it a more suitable option for long-term use, especially in patients with sensitive skin [1,2,3]. This enhanced tolerability encourages consistent use, leading to better treatment outcomes [5].
Conclusion
Trifarotene represents a significant advancement in acne treatment, offering targeted, effective, and well-tolerated therapy. Its selective action provides enhanced efficacy with minimal side effects, distinguishing it from traditional retinoids like tretinoin. Trifarotene’s unique profile makes it a suitable choice for individuals with sensitive skin or those who require a gentler approach.
For those seeking a tailored acne treatment, trifarotene cream offers a promising option. To explore how Monderma’s personalised treatments may enhance your skincare routine, consider completing our free consultation.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- Balak DMW. Topical trifarotene: a new retinoid. British Journal of Dermatology. 2018;179(2):241-242.
- Cosio T, Di Prete M, Gaziano R, et al. Trifarotene: A Current Review and Perspectives in Dermatology. Biomedicines. 2021;9(3):237.
- Brumfiel CM, Patel MH, Bell KA, Cardis MA. Assessing the Safety and Efficacy of Trifarotene in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021;17:755–763.
- Australian Prescriber. Trifarotene for Acne. Aust Prescr. 2021;44(3):101-102.
- Schleicher S, Moore A, Rafal E, et al. Trifarotene Reduces Risk for Atrophic Acne Scars: Results from A Phase 4 Controlled Study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13(12):3085-3096.