 Monderma
Monderma- 22 May 2025
- Folliculitis causes tender bumps
- Inflammation begins within follicles
- Bacteria or yeast may trigger flares
- Care reduces discomfort and scarring
- Personalised skincare with Monderma
Pustular folliculitis can cause discomfort and concern because it affects visible areas of skin. Understanding why it appears helps support calm decisions about treatment and care.
In this article we explore its causes, symptoms, and treatment options to support confident choices through simple, evidence based guidance.
What Is Pustular Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is histologically defined as the presence of inflammatory cells within the hair follicle wall, creating a follicular based pustule, with the type of inflammatory cells varying based on the cause [2].
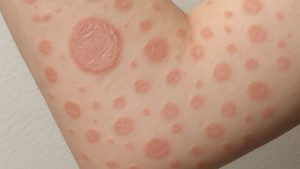
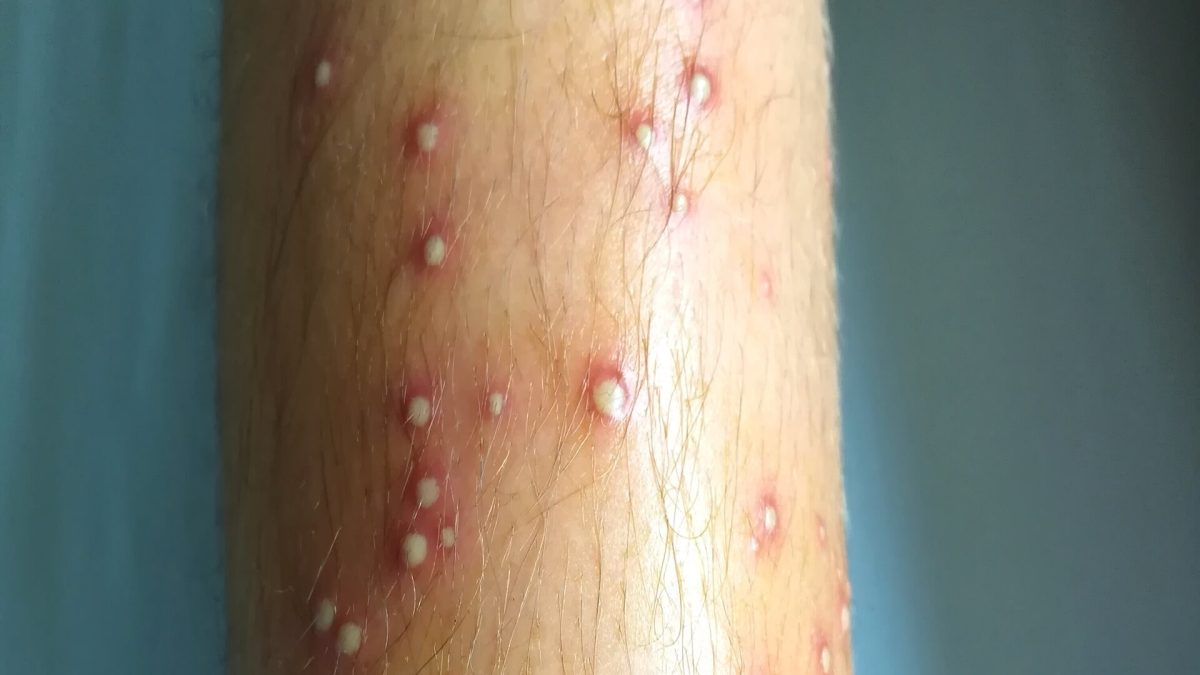
Pustular folliculitis affects hair follicles and produces pus filled bumps. It differs from acne because it begins within follicles and often needs folliculitis cream or shampoo products [1,2].
Mild cases cause irritation while more persistent cases benefit from treatment to support comfort and skin clarity.
Symptoms Of Pustular Folliculitis
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Red, inflamed bumps | Sensitive areas that resemble acne |
| Itching or tenderness | Can lead to scratching and further irritation |
| Pus filled pustules | May rupture and increase infection risk |
| Crusting or scabbing | Appears as pustules heal |
Table 1: Common symptoms
Fact: Pityrosporum folliculitis, caused by Malassezia yeast, presents as itchy, uniform papules and pustules and is distinct from bacterial forms [3,5].
Areas Commonly Affected
| Area | Reason for susceptibility |
|---|---|
| Scalp | Moisture and hair density increase risk |
| Face | Shaving or oiliness may irritate follicles |
| Back | Higher oil production encourages bacteria |
| Chest | Warm conditions increase sweating |
| Thighs | Friction from clothing or exercise |
Table 2: Common locations
Causes Of Pustular Folliculitis
Multiple triggers influence folliculitis, including infections and irritation. Understanding these supports targeted treatment.
Bacterial Infection
Staphylococcus aureus frequently causes bacterial folliculitis. It enters follicles and triggers inflammation and pustules [2,4]. Close contact or shared towels increase risk and recurrent infections may require specific folliculitis antibiotics.
Fact: Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of bacterial folliculitis, with nasal carriage increasing the risk of recurrent infections [1,2,6].
Fungal Infection
Malassezia yeast causes pityrosporum folliculitis. It produces uniform bumps and responds to antifungal treatments rather than antibiotics [3,5].
Fact: Malassezia folliculitis is often misdiagnosed as acne but responds to antifungal therapy, with oral antifungals like ketoconazole or itraconazole effective for pityrosporum folliculitis in a majority of cases [5].
Other Contributing Factors
Friction or irritation from clothing or shaving can inflame follicles [2]. Sweat and heat support bacterial growth, including hot tub folliculitis linked with Pseudomonas aeruginosa [2,4]. A weakened immune system from conditions such as diabetes or HIV increases susceptibility [4,5].
Fact: Hot tub folliculitis, caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is typically self limiting but may require antibiotics in immunocompromised patients [2,4].
Treatment Options For Pustular Folliculitis
Treatment supports comfort by reducing inflammation and addressing specific causes.
Home Care Remedies
Warm compresses may ease irritation by softening debris [2,5]. Gentle cleansers support hygiene without disrupting the skin barrier [1,2].
Medical Treatments
Topical antibiotics like mupirocin treat bacterial folliculitis [1,4,7]. Oral antibiotics such as erythromycin support more widespread cases [4]. Oral and topical antifungals help resolve pityrosporum folliculitis [3,5].
Medicated shampoos with antifungal or antibacterial agents assist with scalp folliculitis [3]. Low dose corticosteroids may reduce severe inflammation [4].
Fact: Topical mupirocin applied to the nasal mucosa twice daily for 5 days can eliminate persistent Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage in most individuals [7].
Over The Counter Options
Folliculitis cream with hydrocortisone may soothe discomfort [2]. Benzoyl peroxide reduces inflammation in mild cases [4].
Preventing Pustular Folliculitis
Comfortable clothing helps reduce friction [2]. Shaving with a clean electric razor can limit irritation [1,4]. Keeping skin dry and clean after sweating supports prevention of hot tub folliculitis [2,4]. A balanced lifestyle promotes immune strength [2].
When To See A Doctor
Seek guidance if symptoms worsen, spread, or persist despite home care. Severe pain, swelling, or fever requires medical support to avoid deeper infection [4].
Conclusion
Pustular folliculitis can improve with attention to triggers such as bacteria, yeast, or irritation, and with treatments that ease inflammation and support clearer follicles. Consistent habits often help maintain comfort and reduce the chance of recurrence.
If you would like personalised skincare created around your own needs, you can explore a tailored formula through Monderma.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- Winters RD, Mitchell M. StatPearls.
- DermNet NZ. Folliculitis.
- Rubenstein RM, Malerich SA. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol.
- BMJ Best Practice. Folliculitis.
- Healthline. Pityrosporum Folliculitis.
- Monderma. Ingredients: Clindamycin.
- Casewell MW, Hill RL. J Antimicrob Chemother.