Monderma
Monderma- 22 Apr 2025
- UV light drives melanin change
- Protection slows pigment increase
- Topicals support clearer tone
- Diet influences skin balance
- Guidance is available with Monderma
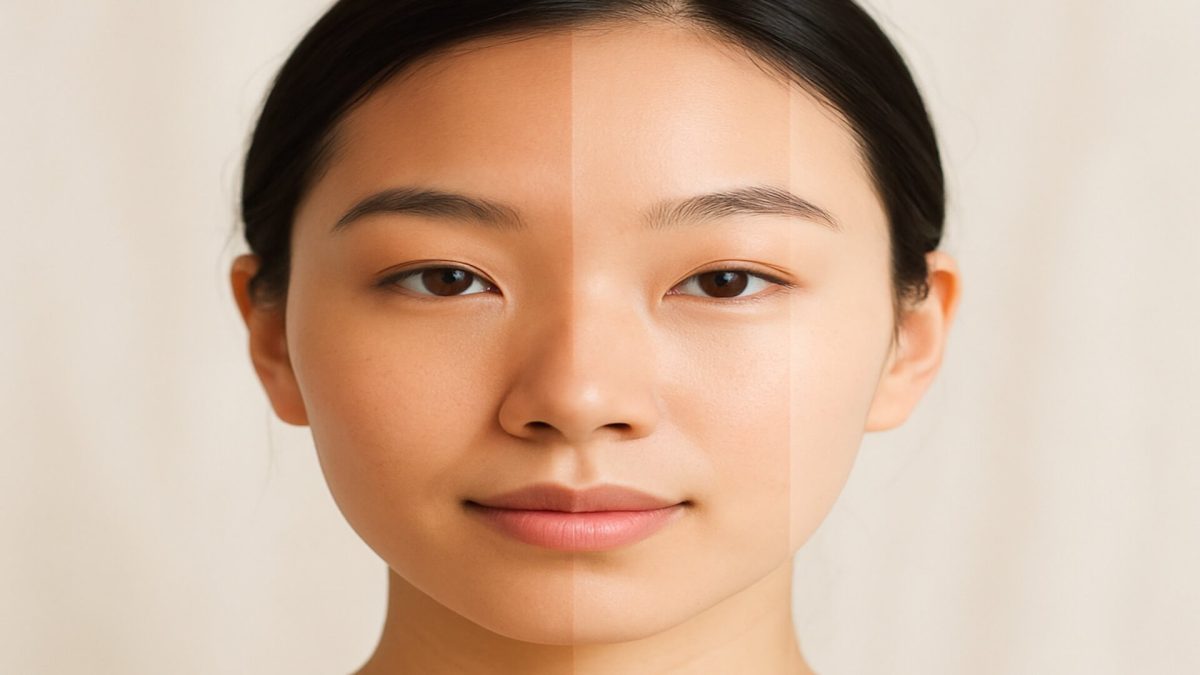
Melanin gives natural defence against sun exposure, yet increased melanin may create concerns such as hyperpigmentation or melasma. These changes often affect confidence, especially when marks deepen with time [1].
In this article, we explain how melanin forms, why it increases, and which approaches support a more even tone. You will see simple, evidence based ways to approach pigmentation safely and effectively.
Understanding Melanin
Melanin forms within melanocytes to protect deeper tissues from UV light. This natural process rises when sunlight increases, which can darken existing pigmentation or trigger new patches [1].
Although protective, excess melanin may contribute to uneven skin tone or persistent marks after inflammation. Gentle, consistent care helps maintain clarity without compromising the skin barrier.
Non Prescription Methods & Protection
Daily sunscreen remains central for those exploring how to lower melanin. UV exposure stimulates pigment production, which steady protection helps reduce over time [1].
Vitamin C inhibits tyrosinase activity, easing pigment formation while supporting brightness. Licorice extract offers a gentle alternative by calming inflammation and helping even the tone [2,3,8].
Topical Approaches
| Method | Summary |
|---|---|
| Sunscreen | Broad spectrum SPF blocks UV signals that increase pigmentation [1] |
| Vitamin C | Reduces melanin synthesis and supports brightness [2,3] |
Table 1: Core non prescription approaches
Additional Options
| Method | Summary |
|---|---|
| Licorice extract | Glabridin lightens dark spots and suits sensitive skin [8] |
Table 2: Additional topical support
Dietary Approaches & Skin Health
Antioxidants from berries, green tea, and leafy greens help reduce oxidative stress. This stress can increase melanin activity, so balanced intake supports a clearer tone [4].
Vitamin E from nuts, seeds, and avocados strengthens barrier health, while hydration improves overall resilience. The NHS recommends one and a half to two litres of water daily for steady skin comfort [5,6].
Dietary Support
| Approach | Summary |
|---|---|
| Antioxidant foods | Reduce oxidative stress that can increase pigmentation [4] |
| Vitamin E | Helps protect skin layers from UV related changes [5] |
Table 3: Dietary benefits
Hydration Role
| Approach | Summary |
|---|---|
| Water intake | Supports clarity and texture with consistent hydration [6] |
Table 4: Hydration guidance
Prescription Treatments & Melanin Control
Hydroquinone remains a leading option for melanin reduction by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. Dermatology oversight ensures safe use, especially when concentrations rise to support melasma care [3].
Retinoids improve pigmentation by increasing cell turnover. These treatments work gradually and require routine monitoring to limit irritation while maintaining long term benefit [7].
Prescription Options
| Treatment | Summary |
|---|---|
| Hydroquinone | Lightens dark patches by reducing melanin formation [3] |
| Retinoids | Increase turnover to fade pigmented cells [7] |
Table 5: Prescription treatments
Professional Interventions & Deeper Care
Chemical peels exfoliate surface pigment with acids such as glycolic acid. This reveals clearer skin with repeated treatments under professional supervision [9].
Laser therapy targets melanin directly, helping improve melasma and post inflammatory pigmentation. Multiple sessions may be required due to variable response [10].
Professional Methods
| Method | Summary |
|---|---|
| Chemical peels | Improve clarity through controlled exfoliation [9] |
| Laser therapy | Breaks down melanin for gradual fading [10] |
Table 6: Professional interventions
Important Considerations
Melanin exists in different forms, including eumelanin and pheomelanin. Both protect the skin from UV harm, so reduction should be approached gently to preserve long term health [1].
Patch testing prevents irritation from new products, while professional review ensures safe ingredient choice. Balanced routines support clearer tone without disrupting natural defences.
Conclusion
Reducing production of melanin can involve sun protection, topical treatments, dietary choices, and professional support. These evidence based approaches help manage hyperpigmentation safely and encourage a more even skin tone.
If you would like personalised skincare that reflects your own needs, you can begin with a custom formula through Monderma.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- Gabros S, Nessel TA, Zito PM. Sunscreens and Photoprotection. StatPearls.
- Darr D, et al. Topical vitamin C protects skin. Br J Dermatol.
- Hollinger JC, Angra K, Halder RM. Natural ingredients for hyperpigmentation. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol.
- Evans JA, Johnson EJ. Phytonutrients in skin health. Nutrients.
- Keen MA, Hassan I. Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J.
- NHS. Water, drinks and hydration.
- Mukherjee S, et al. Retinoids in skin ageing. Clin Interv Aging.
- Yokota T, et al. Licorice extract and melanogenesis. Pigment Cell Res.
- Sarkar R, et al. Chemical peels in melasma. J Cutan Aesthet Surg.
- Liu Y, et al. Melasma treatment comparison. Frontiers in Medicine.
Join the Newsletter
Insights that make your skin feel understood