Monderma
Monderma- 16 Jan 2025
- Tretinoin reduces melasma by 40% in 24 weeks
- Niacinamide lightens dark spots in eight weeks
- Azelaic acid evens tone & calms inflammation
- Monderma blends actives for tailored efficacy
- Vitamin C reduces melanin & brightens skin
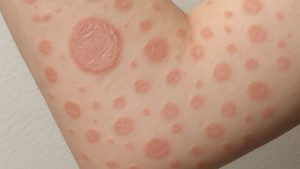
Hyperpigmentation affects people across all skin tones, often presenting as melasma, sunspots, or post-inflammatory marks. These dark patches can make skin appear uneven and dull. Evidence-based skincare ingredients help to fade discolouration safely and effectively when used consistently.
This article reviews proven ingredients for hyperpigmentation and how tailored formulations, such as Monderma’s prescription blends, may support a more even skin tone.
Understanding Hyperpigmentation
What Causes Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin, responsible for skin colour, is produced by melanocytes. Triggers include sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, and inflammation from acne or injury. According to the NHS, UV radiation stimulates melanin production, worsening sun-induced pigmentation [1]. StatPearls reports that hormonal melasma affects up to 50% of pregnant women [2].
Identifying The Type Of Pigmentation
Different forms of hyperpigmentation require tailored care:
- Melasma: Hormonal pigmentation often on cheeks or forehead.
- Sunspots: Caused by long-term UV exposure.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark marks following acne or irritation.
Understanding the cause helps match the right skincare ingredients for optimal results.
Key Ingredients In Hyperpigmentation Creams
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) inhibits tyrosinase, reducing melanin formation and promoting brightness. A 2013 study confirmed that regular vitamin C use visibly lightens dark patches [3]. It also supports photoprotection when combined with sunscreen.
Tretinoin
Tretinoin accelerates skin cell turnover, helping shed pigmented cells. JAMA Dermatology found that 0.05% tretinoin can reduce melasma severity by about 40% after 24 weeks [4]. Because tretinoin may cause mild irritation initially, gradual use is recommended.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide (vitamin B3) reduces melanin transfer and supports the skin barrier. Clinical studies show that 4% niacinamide can decrease dark patches by up to 30% in eight weeks [5]. It is suitable for sensitive skin and enhances tolerance to other active ingredients.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid, derived from grains, helps reduce pigmentation and inflammation. NICE notes that a 20% strength may be effective for hyperpigmentation management [6]. It is gentle and can be used on sensitive or acne-prone skin.
Alpha Arbutin
Alpha arbutin inhibits melanin production without significant irritation [7]. It is suitable for daily use and can complement other brightening agents.
Kojic Acid
Kojic acid suppresses tyrosinase activity, lightening dark spots. Studies confirm its effectiveness in improving uneven tone when used consistently [8].
Adapalene
Adapalene, a synthetic retinoid, promotes cell renewal and helps fade post-inflammatory pigmentation. StatPearls reports 0.1% adapalene reduces PIH within 12 weeks [2].
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone remains one of the most potent topical depigmenting agents. Studies in JAMA Dermatology show 4% hydroquinone can lighten melasma in eight weeks [4]. Because of its strength, medical supervision is advised for safe use.

How Monderma’s Custom Formula Supports Hyperpigmentation Care
Monderma provides individually compounded hyperpigmentation creams containing clinically supported actives such as tretinoin, azelaic acid, adapalene, and hydroquinone.
Consultations are free and reviewed by registered healthcare professionals to ensure safety and suitability. This aligns with NICE guidance recommending individualised treatment plans [6]. Combining ingredients can improve outcomes compared with single agents [9].
Key Ingredients In Monderma Formulations
| Ingredient | What It Is | How It May Help |
|---|---|---|
| Adapalene | Synthetic retinoid | Boosts turnover & evens tone [2]. |
| Azelaic Acid | Naturally derived acid | Reduces pigmentation & inflammation [6]. |
| Hydroquinone | Lightening agent | Lowers melanin for stubborn patches [4]. |
| Niacinamide | Vitamin B3 | Limits pigment transfer & soothes [5]. |
| Tretinoin | Vitamin A derivative | Speeds renewal & fades uneven tone [4]. |
Table 1: Key ingredients in Monderma formulations
Sunscreen For Hyperpigmentation: Essential Protection
Daily sun protection is crucial for preventing and managing pigmentation. The NHS recommends using a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher [1]. For individuals prone to hyperpigmentation, SPF 50 offers additional protection. Sunscreen helps prevent recurrence and maximises the effects of topical treatments.
Choosing The Right Hyperpigmentation Products
Match Your Skin Type
Oily skin may respond well to niacinamide or adapalene. Sensitive skin may prefer azelaic acid or lower retinoid concentrations.
Test New Products
A 24-hour patch test helps identify possible reactions. Discontinue use if redness or irritation develops.
Seek Professional Guidance
Consulting a licensed prescriber or dermatologist ensures appropriate ingredient selection. Monderma’s healthcare team follows clinical guidance from sources such as UpToDate and NICE [6][7].
Enhancing Your Routine With Retinol For Hyperpigmentation
Retinol, a gentler derivative of vitamin A, offers a milder option for those unable to tolerate tretinoin. Regular use promotes smoother texture and reduced discolouration. Combining retinol or tretinoin with daily SPF enhances overall results and reduces risk of irritation.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation can be improved through evidence-based skincare ingredients such as tretinoin, hydroquinone, niacinamide, azelaic acid, and vitamin C. Combining these actives under professional supervision supports more even tone and healthier-looking skin. Consistent use of SPF 50 sunscreen is essential to prevent recurrence.
Those seeking tailored formulations can complete your free Monderma consultation to receive prescription-strength options guided by healthcare professionals.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
Bibliography
- NHS. Sunscreen and sun safety. NHS, accessed 11 July 2025.
- Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation. StatPearls, updated 2023.
- Telang, P.S. Vitamin C in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 2013; 4(2):143–146.
- Kang, W.H. et al. Intermittent therapy for melasma in Asian patients with combined topical agents. J Dermatol. 1998;25(9):587–596.
- Hakozaki, T. et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147(1):20–31.
- Scenario: Management of acne vulgaris in primary care. NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries, 2019.
- Hyperpigmentation disorders: Treatment and management. UpToDate, 2024.
- Lim, J.T. Treatment of Melasma Using Kojic Acid in a Gel Containing Hydroquinone and Glycolic Acid. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25(4):282–284.
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Topical treatment of melasma. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54(4):303–309.
Join the Newsletter
Insights that make your skin feel understood