 Monderma
Monderma- 10 May 2025
- Ingrown hairs cause bumps and redness
- Shaving habits influence trapped hairs
- Exfoliation helps free curled hairs
- Scars may fade with gentle care
- Clearer skin is supported by Monderma
Ingrown hairs are common and can cause visible bumps that feel tender or itchy, which affects daily comfort and confidence across many ages. Learning simple steps supports calmer skin.
In this article you will find clear guidance that explains causes, prevention, and safe removal methods that help maintain smooth, balanced skin.
Understanding Ingrown Hairs
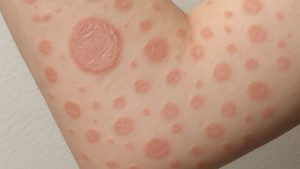
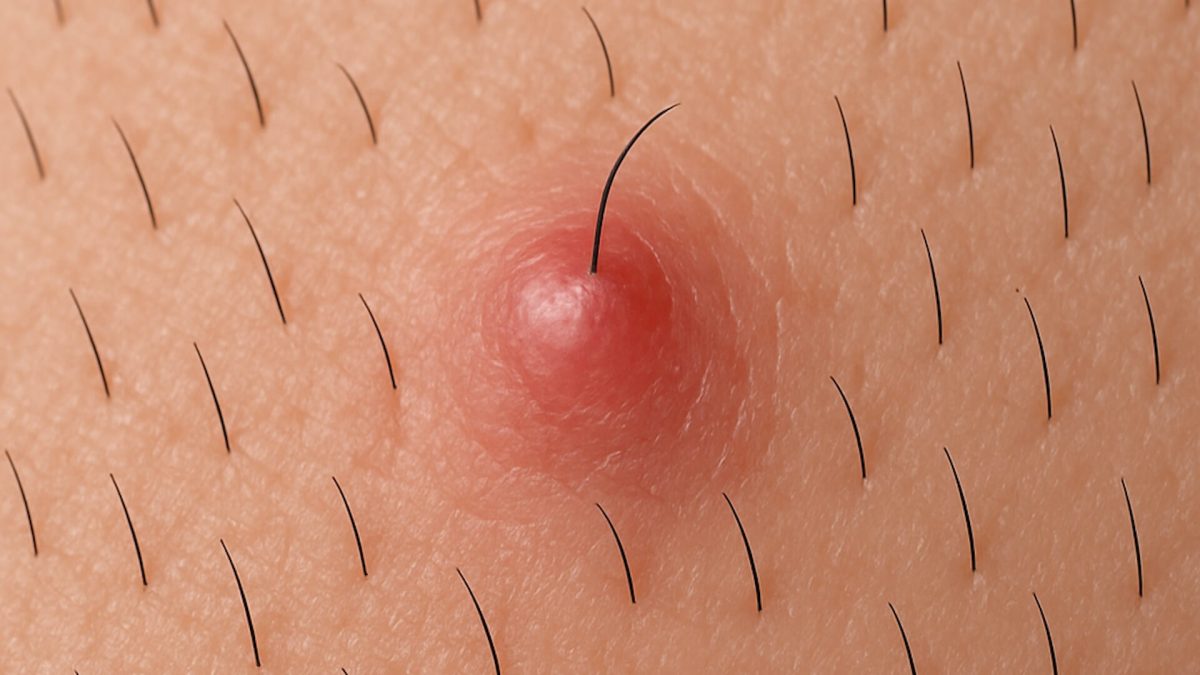
Ingrown hairs happen when a hair curls back into the skin and forms a small raised bump that may feel irritated [1]. This is more common with coarse or curly hair, especially on shaved areas [2].
If untreated, the follicle may become inflamed or infected, which is known as folliculitis, and can cause further discomfort [3].
Causes Of Ingrown Hairs
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Improper shaving techniques | Close shaving or dull blades can create sharp tips that curl into the skin [4] |
| Tight clothing | Friction pushes hairs inward and increases irritation [1] |
| Clogged follicles | Dead skin cells block pathways and redirect growth [5] |
Table 1: Common Causes Of Ingrown Hairs
Preventing Ingrown Hairs After Shaving
Shaving habits strongly influence the chance of trapped hairs, and small adjustments can help reduce bumps [1]. Sharp blades and softening creams support a smoother glide and reduce stress on follicles [4].
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Use the right tools | A sharp razor limits pulling. Creams with soothing agents help reduce friction [4][1] |
| Shaving techniques | Shave with growth and avoid stretching the skin to prevent inward curling [4][1] |
| After shave care | Cold compresses calm skin, while moisturisers support hydration and prevent build up [5] |
Table 2: Shaving Methods That Reduce Ingrown Hairs
Methods To Remove Ingrown Hair
Existing ingrown hairs can be eased with gentle care that frees trapped strands and reduces irritation.
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Exfoliation | Salicylic or glycolic acid helps remove dead cells so the hair can lift free [5][1] |
| Ingrown hair cream | Soothing creams soften skin and support release [5] |
| Ingrown hair serum | Lactic acid or witch hazel helps reduce redness and lift stubborn hairs [5] |
| Tweezing | Only lift visible hairs gently without digging to prevent infection [1] |
Table 3: Methods To Remove Ingrown Hair

Treating Ingrown Hair Scars
Ingrown hairs may leave dark marks or scars, especially in deeper skin tones [2]. Supportive care can calm pigmentation and smooth the appearance of older marks.
| Treatment | Details |
|---|---|
| Topical treatments | Silicone or vitamin E creams may soften scars, while niacinamide supports tone improvement [5][6] |
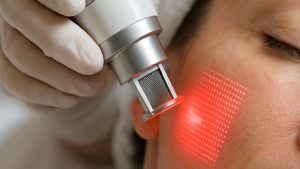
| Professional treatments | Peels refresh the surface, while laser removal reduces regrowth and related scarring [5][2] |
Table 4: Approaches For Ingrown Hair Scars
Additional Prevention Tips
Regular exfoliation keeps follicles clear and reduces build up that leads to trapped hairs [1]. Loose clothing lowers friction on recently shaved skin, and hydration supports softness and flexibility [1][5].
Conclusion
Ingrown hairs are a common concern, yet simple evidence based steps can help reduce irritation and prevent trapped hairs from forming. When symptoms persist or become uncomfortable, professional input can offer clarity and support more predictable results.
If you would like personalised skincare created around your own needs, you can explore a custom formula through Monderma.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- NHS. Ingrown Hairs.
- British Association of Dermatologists. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae.
- Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. StatPearls.
- Jasterzbski TJ, Schwartz RA. Pseudofolliculitis Cutis: A Vexing Disorder of Hair Growth. Br J Dermatol.
- Oakley A. Folliculitis. DermNet NZ.
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, et al. The Effect of Niacinamide on Reducing Cutaneous Pigmentation and Suppression of Melanosome Transfer. Br J Dermatol.
- Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, et al. Retinoids in the Treatment of Skin Aging: An Overview of Clinical Efficacy and Safety. Clin Interv Aging.
Join the Newsletter
Insights that make your skin feel understood