Monderma
Monderma- 13 May 2025
- Eczema causes dryness and irritation
- Creams support barrier repair daily
- Hydrating care reduces flare triggers
- Ingredients calm inflammation gently
- Guides choices when paired with Monderma
Eczema causes dry, itchy, and irritated skin that can disrupt comfort in daily life [1]. Creams for eczema play an important role in easing symptoms and helping the skin feel more settled.
In this article you will find clear guidance that explains common types of eczema, the creams that support relief, and ways to care for sensitive skin during flare patterns.
Understanding Eczema
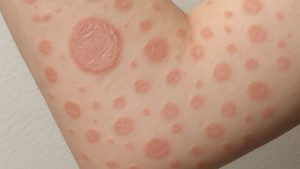
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition with redness, itching, and flare patterns that may begin in childhood [4]. It can affect up to 20 percent of children and around 3 percent of adults [1,4].
Flare triggers include irritants, allergens, soaps, or stress. These triggers often affect areas such as elbows, knees, the face, and flexural areas [1]. Management focuses on barrier repair and calming inflammation.
Types Of Eczema
Eczema varies in presentation, with atopic dermatitis being most common. Contact dermatitis and follicular accentuation can appear as patterns involving papules around hair follicles [4].
Eczema Types
| Type of Eczema | Description |
|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | Most common form with itching and childhood flares [1,4] |
| Contact dermatitis | Triggered by irritants or allergens that cause redness [2] |
| Follicular pattern eczema | Shows papules around hair follicles, especially in children with darker skin [4] |
Table 1: Common eczema types
Choosing The Right Cream
Selecting the right cream depends on symptom severity and skin needs. Key ingredients can support hydration, calm irritation, and protect the skin barrier.
Emollients For Eczema
Emollients for eczema help hydrate and repair the barrier, which reduces flare frequency. NICE notes that emollients are central to long term care, even when skin appears clear [3].
Useful ingredients include glycerin for hydration [5], petroleum jelly for moisture locking [4], and lanolin for protection, though some people may find it irritating [4]. Applying emollients twice daily supports comfort [3].
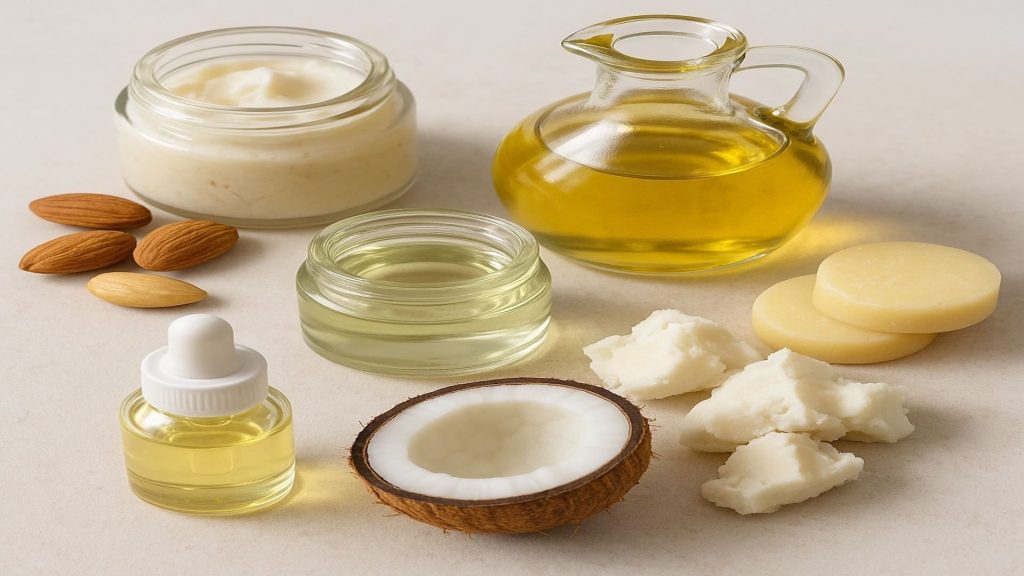

Topical Steroids
Topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation and itching during flares. NICE recommends tailoring potency, with milder options for the face and stronger ones for severe body flares [3].
Overuse may thin the skin, so medical advice is important [2]. A systematic review found that moderate to high potency corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are effective for managing symptoms [6].
Natural Ingredients
Some creams use natural ingredients to soothe reactive skin. Aloe vera offers anti inflammatory support [4], coconut oil hydrates and may reduce bacterial growth [4], and colloidal oatmeal calms irritation [1,4].
Patch testing is recommended since natural ingredients may cause sensitivity in some people [4].
Extra Care For Eczema
Gentle lifestyle adjustments complement topical care. Avoiding irritants such as soaps, detergents, and coarse fabrics may reduce flares [1]. Using gentle soap for eczema supports sensitive areas [1].
Regular emollient application helps maintain hydration [3]. Hydration supports general wellness, though evidence linking water intake with eczema severity is limited [4]. Dermatologist care may assist when symptoms persist [4].
Conclusion
Managing eczema often involves steady moisturising, gentle cleansing, and targeted treatments that help calm irritation and support barrier repair. Identifying triggers and choosing soothing formulations can make daily symptoms more manageable over time.
If you would like personalised skincare shaped around your own needs, you can explore a custom formula through Monderma.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
References
- NHS. Atopic eczema.
- NHS. Contact dermatitis.
- NICE. Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management.
- Nemeth V. Eczema.
- Lodén M, Andersson AC, Lindberg M. A double-blind study comparing the effect of glycerin and urea on dry, eczematous skin in atopic patients.
- Chu DK, Wong AWL, Rayner DG, et al. Topical treatments for atopic dermatitis.