 Monderma
Monderma- 12 Jun 2025
- Clusters of boils form carbuncles
- Bacteria enter deeper skin layers
- Symptoms include swelling and pain
- Care focuses on hygiene and review
- Support options available at Monderma
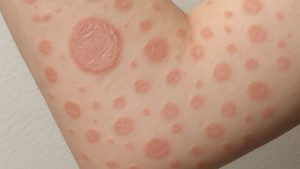
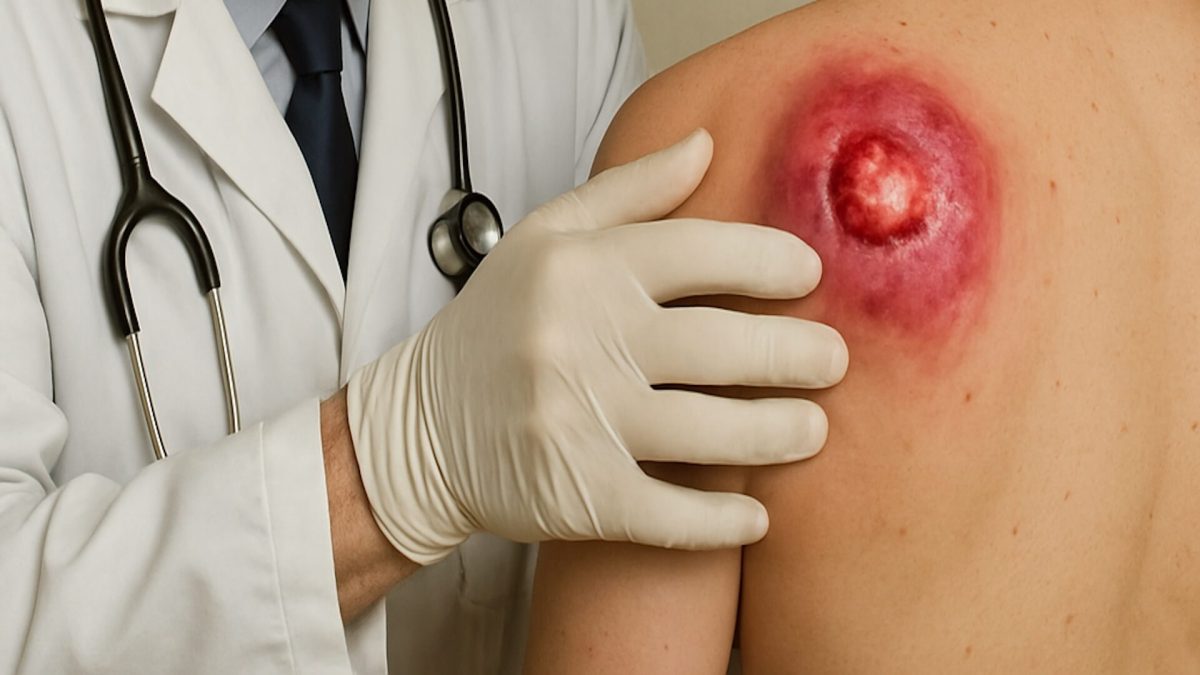
Carbuncles are painful clusters of boils that many people notice during periods of skin stress, and they often arise when bacteria enter deeper layers of skin [1,2,3].
In this article we explain what causes carbuncles, how they present, and why early care helps reduce discomfort, complications, and recurrence.
What Are Carbuncles?
Carbuncles develop when several hair follicles become infected at the same time, creating swollen, pus filled nodules that sit deeper within the skin [1,2,4].
Boils & Carbuncles Compared
Boils involve a single inflamed follicle, while carbuncles represent a wider infection affecting several nearby follicles with greater depth and discomfort [1,2,4].
Causes Of Carbuncles
Staphylococcus aureus commonly triggers these infections, including strains linked with MRSA or PVL producing bacteria [2,4,5]. This organism may live harmlessly on skin until entry points appear [3,4].
Factors That Increase Risk
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Hygiene | Limited cleansing allows bacteria to multiply [2,3]. |
| Weakened Immunity | Diabetes or other conditions reduce defence [2,3]. |
| Skin Issues | Acne or eczema create openings for bacteria [3]. |
| Close Contact | Sharing items increases spread risk [2,3]. |
| Age | More common in teens and young adults [2,3]. |
Table 1: Contributing factors for carbuncles
Symptoms & Diagnosis
Carbuncles appear as red, tender, swollen masses with several drainage points. Some people experience fever or fatigue, and complications such as cellulitis may occur [1,3,4].
Doctors diagnose mainly through clinical appearance, and cultures may be taken in recurrent or severe cases to guide care [2,3,4].
Treatment Approaches
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Home Care | Warm compresses may localise infection and support drainage. Good hygiene lowers spread risk [2,3,4]. |
| Medical Care | Incision and drainage help larger carbuncles. Antibiotics may be needed when symptoms are spreading or systemic [1,4,5]. |
| Monitoring | Rapid or recurrent cases need prompt review [1,4]. |
Table 2: Treatment options
Preventing Carbuncles
Prevention focuses on regular cleansing to reduce bacterial load, avoiding shared personal items, and managing chronic conditions to support skin resilience [3,4].
Skin injuries benefit from gentle cleaning, covering, and ongoing care to prevent bacterial entry. Some recurrent cases may require decolonisation strategies [4,5].
Related Skin Conditions
Folliculitis or hidradenitis suppurativa may look similar at early stages, yet carbuncles are distinguished by depth, pus formation, and the likelihood of systemic symptoms [1,3,4].
Conclusion
Carbuncles can be uncomfortable, but prompt attention, proper hygiene, and appropriate medical care help minimise complications and support faster healing. Understanding triggers and early signs is key to preventing recurrence.
If you would like personalised skincare designed around your own needs, you can explore a tailored formula through Monderma.
References
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
- NHS UK. Infections of the skin
- InformedHealth.org. Overview: Boils and carbuncles
- MedlinePlus. Carbuncle
- StatPearls Publishing. Carbuncle
- Lancet Infect Dis. Panton Valentine leucocidin analysis