- Excess melanin darkens skin patches
- Acne and injuries leave lasting dark spots
- Targeted creams can fade marks in 12 weeks
- SPF 30 daily reduces future pigmentation
- Professional assessment ensures safe, effective treatment
Hyperpigmentation occurs when certain areas of the skin darken due to excess melanin production. It is common and generally harmless, though it can create uneven skin tone.
This article explains the causes, recognised treatments, and skincare steps for managing hyperpigmentation safely.
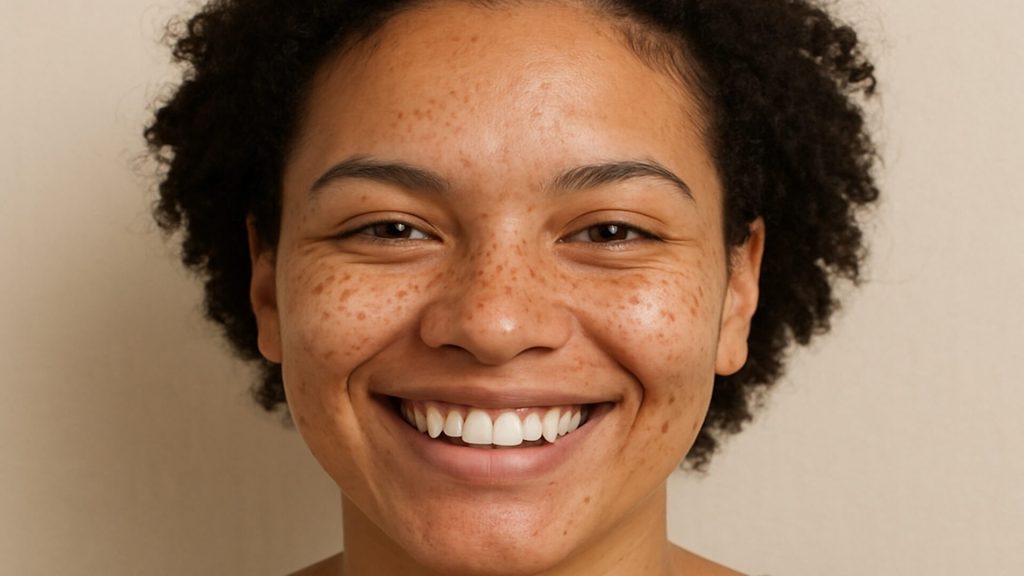

What Causes Hyperpigmentation
Several triggers can cause hyperpigmentation. Identifying these helps guide an appropriate care approach for different skin types.
Sun Exposure
Sunlight is one of the leading causes of hyperpigmentation. UV rays increase melanin production, forming sun spots on areas such as the face and hands.
Continuous exposure can worsen uneven tone, particularly in darker skin types [1]. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher helps protect against this risk [9].
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, including pregnancy or hormonal therapy, can trigger melasma, often called the “mask of pregnancy.” Melasma affects between 8% and 50% of pregnant women, varying by skin tone and location [2].
Broader, symmetrical patches distinguish melasma from other forms. A healthcare professional can recommend suitable management options.
Skin Injuries & Inflammation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation often follows acne, eczema, or minor skin injury. It is particularly common in darker skin tones [3]. Gentle skincare and early treatment support healing and help reduce lingering marks.
Medications
Certain medicines, such as minocycline, may darken the skin as a side effect. Minocycline-related pigmentation occurs in up to 15% of long-term users [4]. If this occurs, seek medical guidance before making changes to treatment.
Genetic Factors
Genetic traits influence the activity of melanocytes and overall pigmentation risk. People with darker complexions often have higher melanin activity [5]. Awareness of family patterns supports preventive skincare planning.
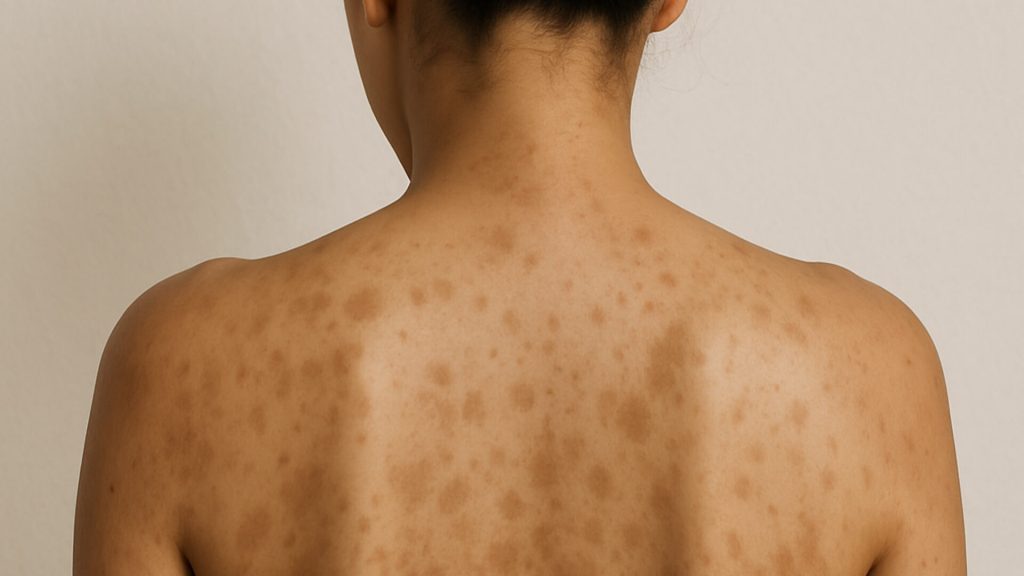
Effective Treatments For Hyperpigmentation
Several treatments can help reduce the appearance of dark spots. Suitability and outcomes depend on the underlying cause, consistency, and professional oversight.
Topical Treatments
Skin creams for hyperpigmentation often include ingredients such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, or vitamin C. Studies show 4% hydroquinone can improve dark patches within 12 weeks [6].
Kojic acid, a natural melanin inhibitor, can enhance skin brightness. Introduce active ingredients gradually to reduce irritation risk.
Hyperpigmentation & Tretinoin
Tretinoin increases cell turnover, helping to fade dark marks and smooth skin texture. It is effective in melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation when used under clinical supervision [12].
As a prescription-only medicine in the UK, tretinoin should be used as directed by a qualified prescriber and always alongside daily sunscreen.
Chemical Peel For Hyperpigmentation
Chemical peels gently exfoliate the skin and improve texture. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels have shown clinical benefit for uneven pigmentation [7].
Post-treatment hydration supports recovery, and a healthcare professional should carry out the procedure.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy targets excess melanin in the skin and can help with stubborn pigmentation cases [8]. It should be performed by trained clinicians, as suitability and outcomes vary.
| Treatment Type | Benefit | Timeframe | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Creams | Lightens dark areas | 8–12 weeks | May cause irritation |
| Tretinoin | Boosts skin renewal | 12–24 weeks | Prescription only |
| Chemical Peels | Improves evenness | 4–8 weeks | Professional procedure |
| Laser Therapy | Reduces persistent marks | 6–12 weeks | Higher cost |
Table 1: Common treatments and considerations
Preventing Hyperpigmentation
Preventive skincare habits protect the skin from new pigmentation and maintain a balanced tone.
Daily Sun Protection
Sunscreen for hyperpigmentation helps prevent dark spots and uneven tone. The NHS recommends broad-spectrum SPF 30, reapplied every two hours outdoors [9]. This step benefits all skin tones and is especially important for those with prior pigmentation issues [10].
Gentle Hyperpigmentation Skincare
A consistent routine using vitamin C, niacinamide, or kojic acid supports skin balance. Antioxidants in skincare and diet can help protect skin cells from oxidative stress [11]. Weekly exfoliation and adequate hydration contribute to smoother, healthier-looking skin.
Monderma’s Custom Formula For Hyperpigmentation
Monderma provides prescription-strength formulations created by UK-registered clinicians and dispensed by a GPhC-registered pharmacy. Each treatment is tailored to individual skin needs after a clinical review.
| Ingredient | Strength | Description | How It Supports Even Tone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapalene | 0.1–0.3% | Vitamin A retinoid | Promotes cell renewal & reduces new marks |
| Azelaic Acid | 3–20% | Naturally derived acid | Helps reduce melanin activity & refine tone |
| Hydroquinone | 2–4% | Prescription-only agent | Reduces melanin formation under supervision |
| Niacinamide | 2–4% | Vitamin B3 derivative | Supports brightness & decreases pigment transfer |
| Tretinoin | 0.01–0.1% | Prescription retinoid | Increases turnover & improves uneven tone |
Table 2: Key ingredients and their benefits for even skin tone
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation can often be managed through consistent skincare, professional assessment, and daily sun protection. Evidence-based ingredients such as hydroquinone, azelaic acid, and tretinoin may help improve uneven tone when clinically appropriate.
You can complete a quick, free online consultation reviewed by a GPhC-registered prescriber to see if a prescription-strength formula could be right for your skin.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
Bibliography
- Del Bino, S. et al. “Variations in skin colour and the biological consequences of ultraviolet radiation exposure.” British Journal of Dermatology, 2013, 169(s3):33-40.
- Ogbechie-Godec, O.A. “Melasma: an Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review.” Dermatology Research and Practice, 2017.
- Davis E.C., Callender V.D. “Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of colour.” Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2010; 3(7):20-31.
- Eisen D., Hakim M.D. “Minocycline-induced pigmentation. Incidence, prevention and management.” Drug Safety, 1998; 18(6):431-440.
- Bajpai, V.K., et al. “A genome-wide genetic screen uncovers novel regulators of melanogenesis.” bioRxiv, 2021.
- Monteiro, R.C., et al. “A Comparative Study of the Efficacy of 4% Hydroquinone vs 0.75% Kojic Acid Cream in the Treatment of Melasma.” Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2012.
- Sitohang, I.B.S., et al. “Trichloroacetic Acid Peeling for Treating Photoaging: A Systematic Review.” Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 2021.
- Sarkar R., Gokhale N., Godse K., et al. “Lasers in Melasma: A Review with Consensus Recommendations by the Pigmentary Disorders Society (PDS), India.” Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2017; 10(1):34-45.
- NHS. “Sunscreen and Sun Safety,” 2025.
- Fatima, S., et al. “The Role of Sunscreen in Melasma and Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation.” Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2020.
- Addor, F.A.S. “Antioxidants in Dermatology.” Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 2013, 27(Suppl 1):19-23.
- Moolla S., Miller-Monthrope Y. “Dermatology: How to Manage Facial Hyperpigmentation in Skin of Colour.” Canadian Family Physician, 2022; 68(5):357-359.
Find your perfect skincare formula
Takes less than 2 minutes – see what your skin needs
Get Custom Formula