- Melasma causes dark skin patches triggered by hormones or sun
- Hydroquinone lightens pigmentation within 4–8 weeks
- Daily SPF 30+ is vital for safe, effective results
- Expert guidance ensures minimal irritation and best outcomes
- Azelaic acid and peels offer gentle alternatives
Melasma is a common pigmentation disorder marked by brown or grey patches on the face. While harmless, its visibility often affects confidence and emotional well-being.
In this article, we explore hydroquinone’s role as the gold standard for fading dark patches and restoring an even skin tone, including how it works and safe ways to use it for brighter, clearer skin.
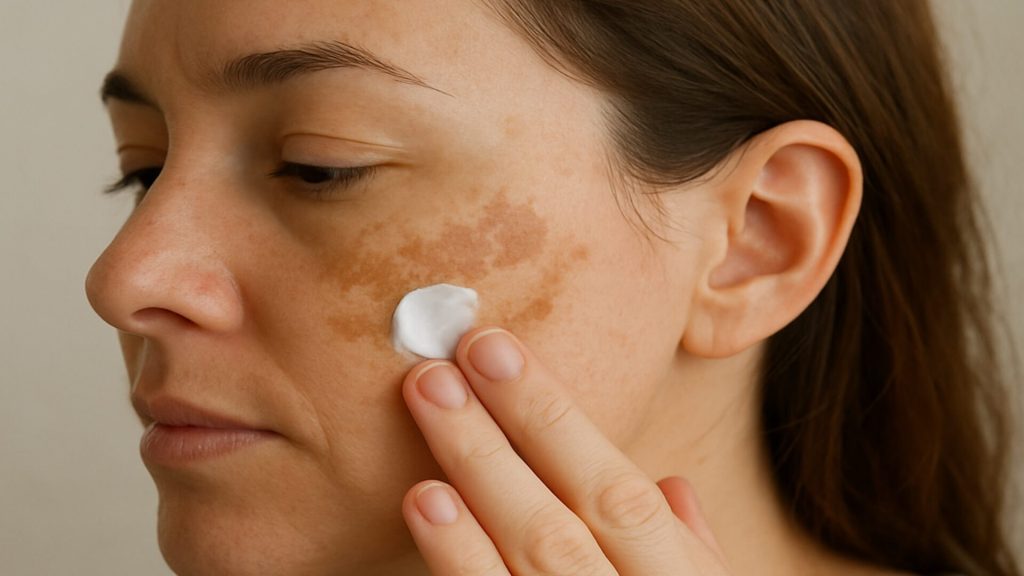

Causes & Triggers Of Melasma
Hormones, Sun & Genetics
Melasma often develops due to hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or contraceptive use. Between 10–50% of pregnant women experience melasma, sometimes called the mask of pregnancy [1]. Genetic predisposition also plays a strong role, especially in individuals with darker skin tones [2,7].
The Role Of Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulates melanocytes, increasing melanin production and worsening dark patches. Melasma tends to intensify during summer [3].
Using broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen daily is essential to prevent flare-ups and enhance treatment success [4].
| Trigger | Effect on Skin | Management Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal changes | Stimulate melanin production | Consult about hormonal control options |
| Sun exposure | Deepens pigmentation | Use SPF 30+ daily |
| Genetics | Increases melasma risk | Use long-term maintenance care |
Table 1: Common melasma triggers and recommended management strategies
Emotional & Psychological Effects
Melasma can significantly affect confidence and quality of life. Over 50% of patients report psychological distress related to their appearance [7,8].
Addressing pigmentation not only improves skin tone but also supports mental well-being and self-assurance.
How Hydroquinone Works
Mechanism of Action
Hydroquinone inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme essential for melanin synthesis. By reducing pigment production, it gradually lightens dark patches.
Topical strengths between 2% and 4% are widely used, with visible improvement typically seen after 4–8 weeks of consistent application [2,5].
Duration & Effectiveness
Patients often notice early lightening within 2–4 weeks, with significant improvement by 8–12 weeks [2,4,5]. Maintenance therapy, combined with sunscreen, helps preserve results.
| Strength | Time to Noticeable Results | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| 2% | 6–8 weeks | Mild pigmentation |
| 4% | 4–6 weeks | Moderate to severe melasma |
Table 2: Typical hydroquinone strengths and expected treatment results
Using Hydroquinone Safely
Overuse or incorrect application can lead to redness or irritation, especially in sensitive skin types.
To use safely:
- Apply only to affected areas.
- Use moisturiser to reduce dryness or stinging.
- Always apply SPF 30+ daily to prevent rebound pigmentation.
- Conduct a patch test before full application [3,4].
Monderma’s licensed prescribers provide clear guidance on safe use and concentrations tailored to your skin type via a free consultation.
Why Hydroquinone Is A Leading Option
Proven Results
Clinical evidence supports hydroquinone’s success. A 2013 study found 4% hydroquinone reduced melasma severity in 80% of patients within 12 weeks [5].
Fast-Acting & Accessible
It acts faster than many alternatives, offering visible improvement and confidence boosts within weeks. Monderma enhances these results through custom blends combining hydroquinone with hydrating actives like hyaluronic acid.
Hydroquinone Vs. Other Melasma Treatments
Azelaic Acid
Derived from grains, azelaic acid (20%) reduces melanin and inflammation. A 2023 study showed it effectively improved melasma while causing fewer side effects than hydroquinone [11].
Best for sensitive or reactive skin.
Chemical Peels
Glycolic or lactic acid peels exfoliate surface cells, complementing hydroquinone. Studies show up to 60% improvement in pigmentation when used together under professional guidance [6].
| Treatment | Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroquinone | Inhibits melanin enzyme | Fast, targeted lightening |
| Azelaic Acid | Reduces pigment & inflammation | Sensitive skin |
| Chemical Peels | Boosts cell turnover | Stubborn pigmentation |
Table 3: Comparative treatments for pigmentation and their best uses

Hydroquinone Before & After Timeline
| Timeline | Expected Results |
|---|---|
| 2–4 Weeks | Subtle fading of dark patches |
| 8–12 Weeks | Noticeable reduction and even tone |
| 12+ Weeks | Maintenance phase with ongoing protection |
Table 4: Hydroquinone treatment timeline and expected results
Monderma’s Personalised Skincare Solutions
Monderma offers prescription-strength skincare tailored for melasma, acne, and pigmentation concerns. Custom formulas may include hydroquinone, azelaic acid, and niacinamide, developed by GPhC-registered prescribers for both safe and effective use.
Conclusion
Hydroquinone remains the most effective treatment for melasma, offering rapid, targeted results through melanin inhibition. When paired with consistent sun protection, gentle skincare, and professional oversight, it delivers safe, lasting improvements in skin tone and confidence.
For expert-led, prescription-based care, visit Monderma’s free consultation portal to discover a treatment designed specifically for your skin’s needs.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
Bibliography
- Handel AC, Miot LDB, Miot HA. Melasma: A Clinical and Epidemiological Review. An Bras Dermatol. 2014.
- Jo JY, Kim JE, Park YW, Lee JH. Update on Melasma Treatments. Ann Dermatol. 2024.
- British Skin Foundation. Melasma. 2020.
- Albzea W, Algarni AA, Alzubaidi H, et al. Azelaic Acid Versus Hydroquinone for Managing Melasma. Cureus. 2023.
- Monteiro RC, Moura HH, Dantas DC, et al. Comparative Study of Hydroquinone and Kojic Acid Cream. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013.
- Garg S, Sarkar R, Mysore V, et al. Chemical Peels in Melasma: Consensus Recommendations. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2017.
- Majid I, Aleem S. Melasma: Update on Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, and Scoring. J Skin Stem Cell. 2022.
- Platsidaki E, Markantoni V, Nicolaidou E, et al. Self-Esteem, Depression, Anxiety and Quality of Life in Melasma Patients. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023.
Find your perfect skincare formula
Takes less than 2 minutes – see what your skin needs
Get Custom Formula