- Papules are small, raised skin bumps
- They appear in acne, eczema, or psoriasis
- Usually harmless but may need assessment
- Identify triggers and manage inflammation early
- Professional care ensures accurate diagnosis
Papules are small, raised bumps that appear in many common skin conditions. Though they can look concerning, most are harmless. These tiny lesions can vary in colour and texture, appearing anywhere on the body. Understanding what causes papules helps determine if they are temporary irritations or signs of something requiring medical attention.
This article explores papules, how they form, conditions that cause them, and the differences between papules, moles, and warts.
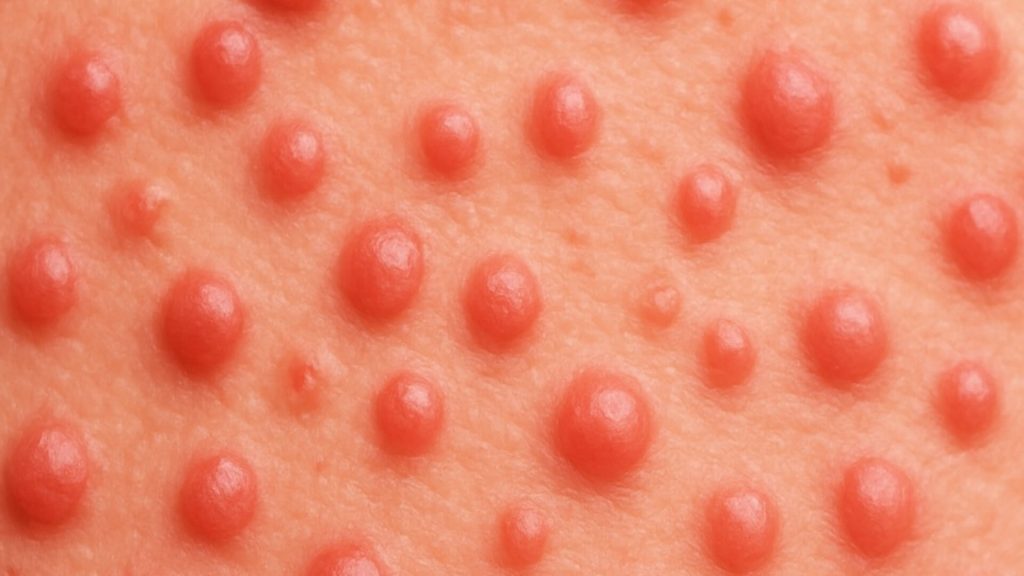
What Are Papules
Papules are small, solid skin bumps under 1 cm in diameter [1,2]. They contain no pus or fluid, unlike pustules or vesicles [3]. Papules can appear as red, brown, purple, or flesh-toned, and may have a smooth or rough surface [3].
Recognising their appearance helps distinguish them from other skin lesions and supports early identification of potential causes.
How Papules Form
Papules develop from irritation or inflammation that causes localised swelling of the skin [4]. This occurs when the immune system reacts to internal or external triggers such as infections, allergies, or chronic skin conditions [5].
Common Triggers Include
- Blocked pores or bacterial infection
- Skin irritation from harsh skincare products
- Sun exposure or environmental pollutants
- Hormonal changes or high stress levels [6]
Identifying these triggers supports prevention and helps guide gentle, evidence-based care.
Common Skin Conditions & Papules
Papules are common in several dermatological conditions. Each condition presents differently and may require specific management approaches.
| Skin Condition | Characteristics | Common Locations | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acne | Inflamed bumps caused by clogged pores that may progress to pustules or nodules [7]. | Face, back, shoulders | Topical benzoyl peroxide or retinoids; skincare adjustments; lifestyle changes [8]. |
| Eczema | Dry, itchy skin with red papules during flare-ups [9]. | Elbows, knees, face | Use emollients, mild corticosteroids, and avoid triggers [10]. |
| Psoriasis | Red, scaly papules merging into plaques due to immune activation [11]. | Elbows, knees, scalp | Apply topical agents, phototherapy, or prescribed systemic treatments [12]. |
| Lichen Planus | Purple, itchy, flat-topped papules that may appear in clusters [13]. | Wrists, ankles, mouth | Topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or light therapy [14]. |
Table 1: Common skin conditions associated with papules and their management
Differentiating Papules From Other Skin Lesions
Papules can resemble other lesions such as moles, warts, or nodules. Recognising their differences helps guide accurate assessment and care.
| Lesion Type | Characteristics | Cause | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moles | Pigmented, stable skin growths that can change with time; sudden changes may require review [15]. | Melanocytes | Regular monitoring or excision if clinically necessary [16]. |
| Warts | Rough, raised bumps with a cauliflower-like surface; spread through HPV [17]. | Viral infection | Topical wart treatments or cryotherapy under supervision [18]. |
| Nodules | Larger, deeper, solid lumps beneath the skin’s surface [19]. | Varies by condition | Dermatologist assessment; sometimes medication or surgery [20]. |
Table 2: Differences between papules and other common skin lesions
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most papules heal naturally, but medical advice may be needed if:
- They rapidly change in size, shape, or colour [16].
- They become painful, itchy, or inflamed [5].
- Other symptoms such as fever or fatigue appear [4].
Early professional assessment can help rule out infection or more serious conditions [21].
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Dermatologists or healthcare professionals can recommend suitable care.
Topical Treatments
Mild acne-related papules may respond to benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid [8]. Prescription retinoids such as tretinoin may help reduce blocked pores and inflammation [22].
Moisturisers & Creams
For eczema or psoriasis, emollients and mild corticosteroids reduce dryness and irritation [10,12]. Azelaic acid can be used to help manage inflammation and redness associated with rosacea [23].
Medical Procedures
Stubborn lesions like warts may require dermatological treatments such as cryotherapy or laser therapy, performed safely by qualified professionals [18].
Monderma’s Role In Personalised Skincare
Monderma provides prescription skincare designed for acne, rosacea, hyperpigmentation, and other skin concerns. After a free online consultation, healthcare professionals formulate treatments using evidence-based ingredients such as azelaic acid, niacinamide, or tretinoin.
This personalised approach supports safe, effective management tailored to individual skin types. Learn more through Monderma’s free online consultation.
Conclusion
Papules are small, raised lesions that often result from inflammation or common skin conditions such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis. Most are harmless, but persistent or changing papules should be reviewed by a healthcare professional.
With professional support and tailored skincare, managing papules becomes more straightforward. Explore Monderma’s free consultation service to discover personalised options for clearer, balanced skin.
Content is for informational purposes only. Monderma treatments are prescribed following consultation. Results and timeframes can vary. Use as directed by your prescriber.
Bibliography
- Nast A, et al. Papule. In: ScienceDirect Topics. 2016.
- Habif TP. Clinical Dermatology. 6th ed. Elsevier; 2015.
- Marks JG, Miller JJ. Lookingbill and Marks’ Principles of Dermatology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2013.
- Bolognia JL, et al. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
- Goldsmith LA, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2012.
- Draelos ZD. Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures. Wiley-Blackwell; 2015.
- Zaenglein AL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(5):945-973.
- NICE. Acne vulgaris: management. 2021.
- Eichenfield LF, et al. Guidelines of care for atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(2):338-351.
- NICE. Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management. 2007.
- Menter A, et al. Guidelines of care for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):826-850.
- NICE. Psoriasis: assessment and management. 2012.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):723-732.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Lichen planus: Diagnosis and treatment. 2025.
- Bolognia JL, et al. Melanocytic nevi and neoplasms. In: Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
- UpToDate. Melanoma: Clinical features and diagnosis. 2023.
- Sterling JC, et al. British Association of Dermatologists’ guidelines for the management of cutaneous warts. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171(4):696-712.
- Sabry AO, Patel BC. Papillomas: A Multisystem Overview of HPV-Associated and HPV-Independent Lesions. StatPearls. 2023.
- DermNet NZ. Terminology in dermatology. 2025.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Find skin cancer: How to perform a skin self-exam. 2023.
- NHS. Itchy Skin. 2023.
- Leyden JJ, Stein-Gold L, Weiss J. Why topical retinoids are mainstay therapy for acne. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7(3):293–304.
- Thiboutot D, et al. Standard management options for rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(6):1501-1510.
Find your perfect skincare formula
Takes less than 2 minutes – see what your skin needs
Get Custom Formula